Competing with ChatGPT and Bing: Google launches its Bard chatbot
As of 21 March, Google has opened limited access to its chatbot called Bard. For now, it is only available to US and UK users who can sign up to a waiting list on the website.
Here's How It Works
It's a competitor to OpenAI's ChatGPT and Microsoft's Bing, which works along similar lines: you ask a question, a neural network gives you an answer. It's built on LaMDA's language model and looks like it needs some work, but the Google team has decided to launch a full-fledged chatbot access nevertheless.
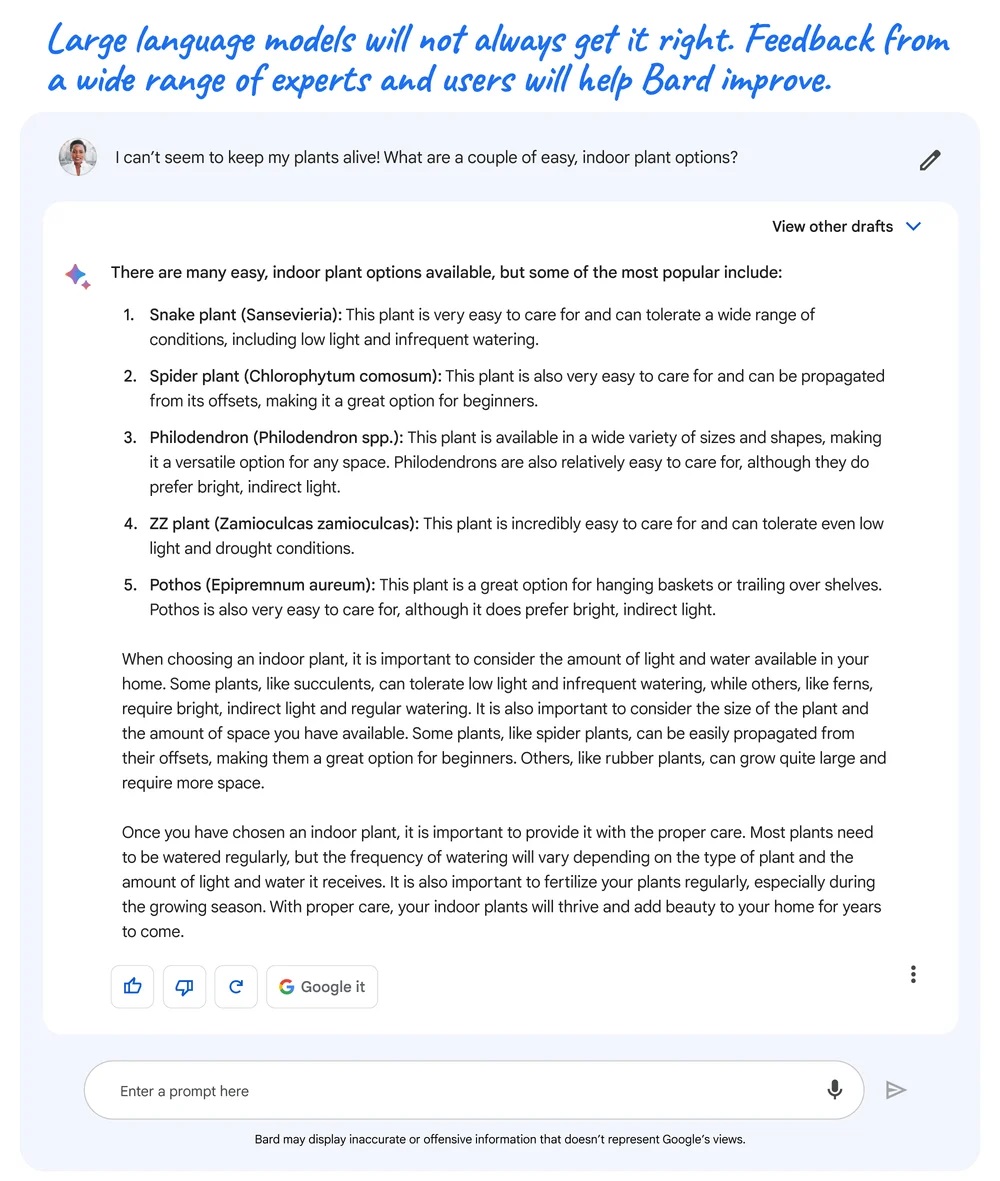
Bard is capable of generating ideas, writing texts or simply being a tool for communication. Google stresses that it is not a substitute for a search engine - we already know that such chatbots can sometimes produce inaccurate information. So when giving answers, the artificial intelligence prompts you to click on Google It to see the results of your query on the search engine.

Also, unlike Microsoft Bing, Bard is far from always providing links to information sources.
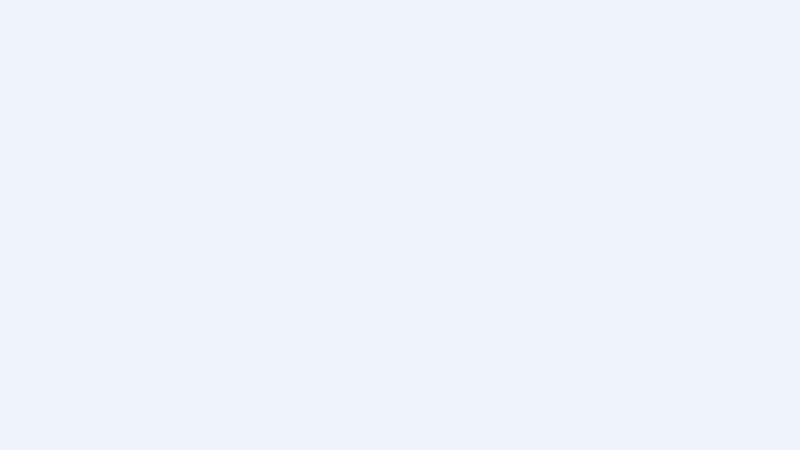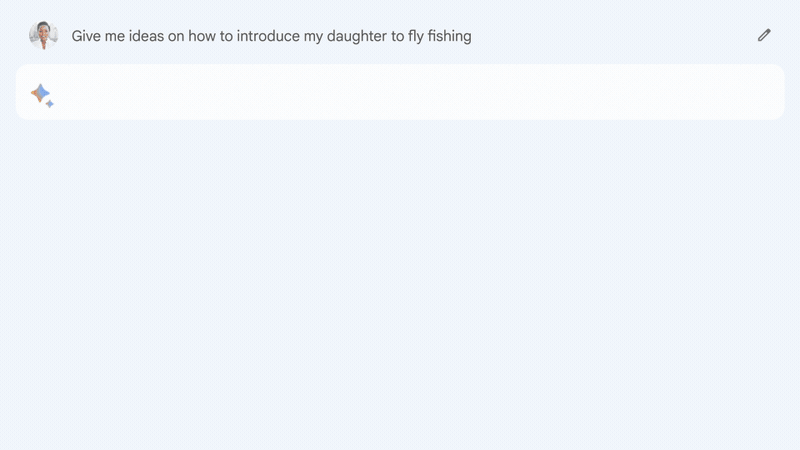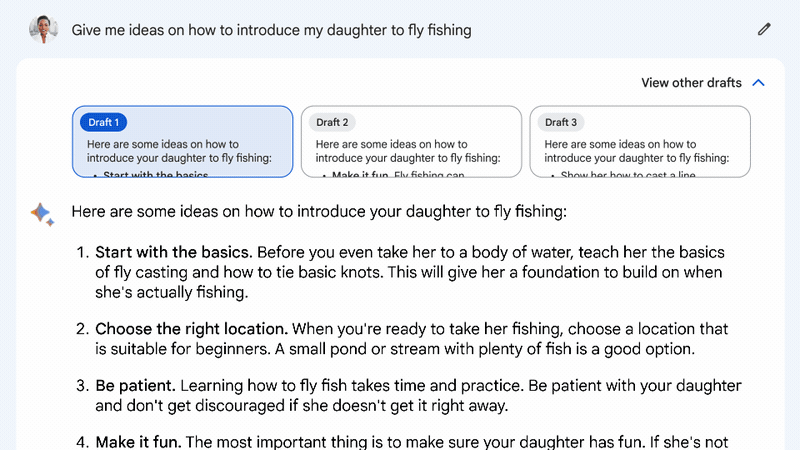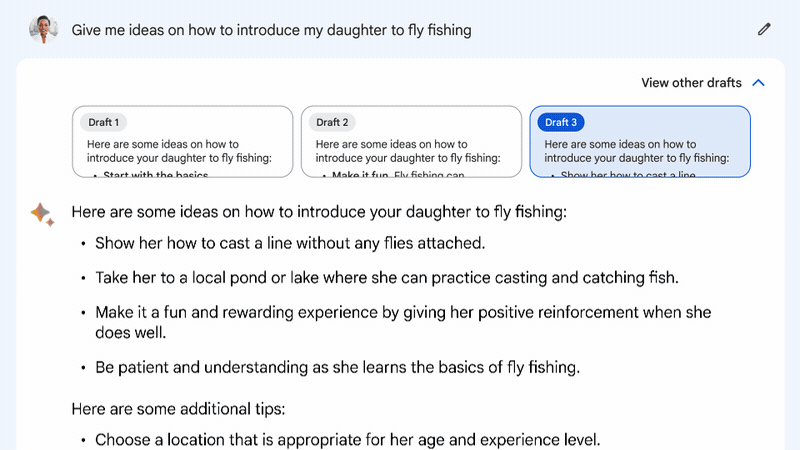
Journalists at The Verge have already had a chance to test Bard and appreciated its fast performance: the chatbot, unlike its competitors, responds much faster to questions, but that may be due to the limited number of users.
The publication put the neural network to the test - not without tricky questions. For example, the journalists offered to "provide five reasons why Crimea should be considered part of Russia". Bard did not pass the test: first he offered answers like "Russia has a long history of owning Crimea", and then he added: "it is important to note that Russia's annexation of Crimea is widely considered illegal and illegitimate".
The Google chatbot will be available in other countries in the future.