Exploring the Viewing Range of Binoculars
Binoculars, those remarkable instruments, transform our view of the world, bringing distant scenes into sharp, impressive detail. Whether you're an avid birdwatcher, a hunter, a sports enthusiast, or captivated by the stars, binoculars are indispensable for enhancing your enjoyment and engagement in your favorite pastimes.
But what's behind their magic? How do they work, and what influences their viewing capabilities? In this detailed exploration, we'll delve into the intricacies of binocular magnification, field of view, and viewing range, unraveling how these elements interplay.
We'll guide you through the various magnification ranges, pinpointing their ideal applications, and aid you in selecting the perfect pair for your adventures. And for those keen on long-distance viewing, we'll uncover the secrets of long-range binoculars and their ability to bring the farthest objects within your sight.
Short answer:The viewing range of binoculars refers to the maximum distance at which you can clearly and comfortably observe objects using the binoculars. It depends on factors like the binoculars' magnification, objective lens diameter, field of view, and atmospheric conditions. Higher magnification typically offers more detail but can reduce the viewing range due to a narrower field of view.
- The Magic of Binocular Magnification
- The Broad View: Binocular Field of View and Viewing Range
- Ideal Uses for Different Magnification Ranges
- Long-Range Binocular Capabilities
- FAQ about Viewing Range of Binoculars
The Magic of Binocular Magnification

Magnification in binoculars is like a superpower for your eyes. It brings distant objects closer, revealing details invisible to the naked eye. When you see a pair marked as 10x, it means it makes things appear ten times nearer. However, magnification is a double-edged sword: while it brings distant objects into focus, it narrows your field of view and can dim your image.
Conversely, lower magnification offers a broader view and brighter images but with less detail. Just so you know, if interesting binocular models are what you're after, here are our four best picks for 2026:
- High-End Performance at Affordable Price
- Ideal for Hunting, Birding, and Wildlife Viewing
- Enhanced Low-Light Performance
- Tack-Sharp Edge-to-Edge Vision with Deep Field
- Compact and Lightweight with Improved Light Transmission
- ED Glass Lenses Minimize Distortion
- Ideal for Birding and Wildlife Observation
- Rubber-Armored, Non-Slip Grip Design
- Waterproof and Fog-Proof for Reliable Performance
- Turn-and-Slide Rubber Eyecups for Eyeglass Compatibility
- HD Lens System for Vivid Imaging
- Best for Birdwatching and Nature Observation
- LotuTec Coatings for Scratch Protection
- Conveniently Placed Focusing Wheel for Easy Use
- Perfect for Stalking Game and Rough Terrain
- Exceptional Clarity and Color Fidelity
- Resistant to Water and Fog
- Eyecups Adjustable for Eyeglass Wearers
- Secure, Non-Slip Rubber Armor
- Includes GlassPak Harness for Easy Carrying
The Broad View: Binocular Field of View and Viewing Range
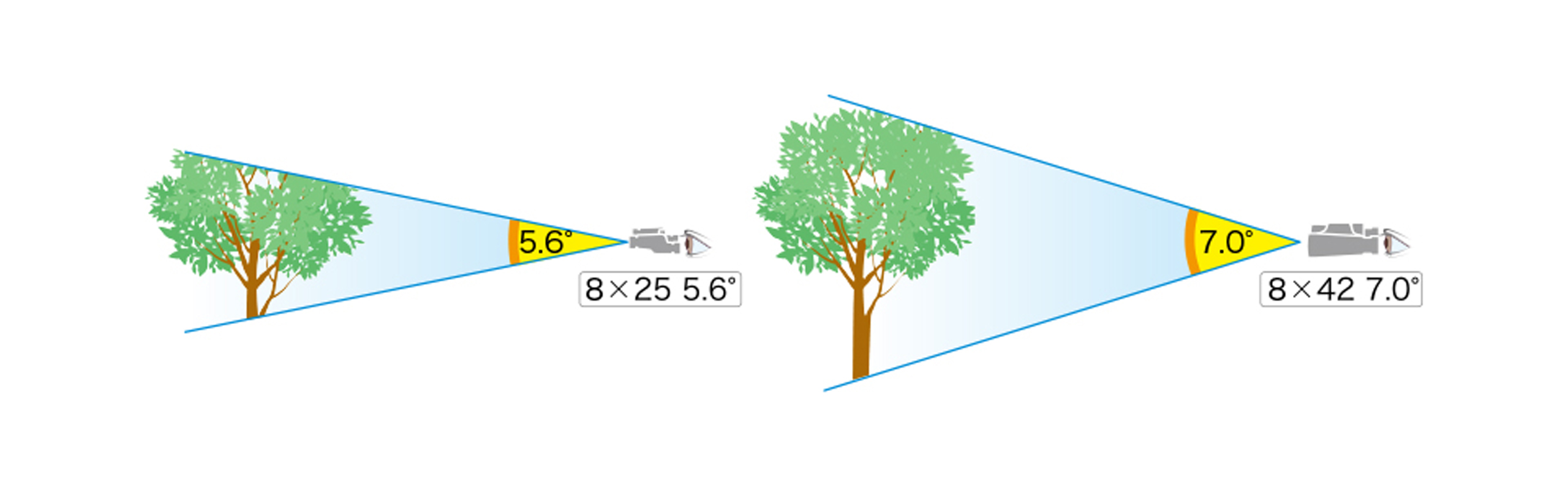
The field of view is the width of the area you can see through your binoculars at a specific distance. It's often measured in degrees or as a width at 1,000 yards. A wide field of view is crucial for following moving objects, like birds or athletes, but a narrower view gives you a more magnified image.
The viewing range is how far you can see clearly with binoculars, influenced by magnification, field of view, lens diameter, and even atmospheric conditions. Higher magnification typically means a shorter viewing range. Larger lenses gather more light, brightening the image and extending your viewing range, especially in dim conditions. But remember, larger lenses add weight and bulk.
Ideal Uses for Different Magnification Ranges
Selecting the perfect binoculars hinges on understanding different magnification ranges and their specific applications:
| Magnification Range | Description | Ideal Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Low (2x to 7x) | Wide field of view, bright and stable images without stabilization devices. Excellent for low-light conditions. | Ideal for birdwatching, sports events, and nature observation. They allow easy tracking of fast-moving subjects and are great for viewing large or nearby objects like landscapes and wildlife. |
| Medium (8x to 12x) | Balanced between detail and field of view. Offer more magnification than low range while maintaining a respectable viewing width. | Perfect for birdwatching and wildlife observation for better detail in identifying and studying animals. Also suitable for hunting, boating, and hiking, offering a good mix of power and portability. |
| High (13x and above) | Provide the most detail and the longest viewing range, but have the narrowest field of view and dimmest image. Require stabilization devices like tripods. | Ideal for long-range observation activities such as astronomy, surveillance, or long-distance shooting. Allow viewing of faraway objects and detailed observation of small or distant items. |
Long-Range Binocular Capabilities

Long-range binoculars, like 20x80s, are your ticket to viewing distant celestial bodies or minute details on far-off mountains. They let you witness the moon's craters or Jupiter's moons but have limitations, like a narrow field of view and dimmer images in low light.
FAQ about Viewing Range of Binoculars
How does the atmospheric condition affect the viewing range of binoculars?
The atmospheric condition, such as the temperature, humidity, air pressure, and pollution, can affect the viewing range of binoculars by causing distortion, glare, or haze in the image, reducing the clarity and the contrast. The best viewing range of binoculars is achieved in clear, dry, and calm weather.
What is the difference between viewing range and field of view?
Viewing range is the distance from the nearest to the farthest point that can be seen clearly through the binoculars. Field of view is the area of the sky or the landscape that can be seen through the binoculars at a given distance. Viewing range and field of view are inversely related, meaning that as one increases, the other decreases.
How can I improve the viewing range of my binoculars?
You can improve the viewing range of your binoculars by choosing the right magnification, objective lens diameter, exit pupil, and eye relief for your needs and preferences. You can also use stabilization devices, such as tripods or monopods, to avoid image shake and blur.
You can also adjust the focus, the diopter, and the interpupillary distance of your binoculars to match your eyesight. You can also clean and maintain your binoculars regularly to prevent dust, dirt, or moisture from affecting the image quality.
Viewing Range of Binoculars: Conclusion
Binoculars are a gateway to a more vivid, detailed world, whether you're gazing at distant galaxies or nearby wildlife. Choosing the right pair involves balancing your needs with the binoculars' specifications and testing various models to find your perfect match. With the right binoculars in hand, the wonders of the world are yours to behold.
You may also like:




