Disc Brakes on E-Bikes
Disc brakes have become increasingly popular on electric bikes, offering superior stopping power, better modulation, and improved performance in various weather conditions compared to traditional rim brakes. As e-bikes continue to evolve and riders venture into more challenging terrains, understanding the benefits and maintenance requirements of disc brakes is crucial for a safe and enjoyable riding experience.
Short answer: Disc brakes on e-bikes provide enhanced stopping power, better modulation, and more consistent performance in wet conditions compared to rim brakes. They come in two main types: mechanical and hydraulic, each with its own advantages and maintenance needs. Regular upkeep, including cleaning, replacing pads, and aligning rotors, is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
- Types of Disc Brakes
- Benefits of Disc Brakes on E-Bikes
- Maintaining Your Disc Brakes
- Disc Brake Maintenance Tips
- Disc Brakes on E-Bikes: FAQ
Types of Disc Brakes
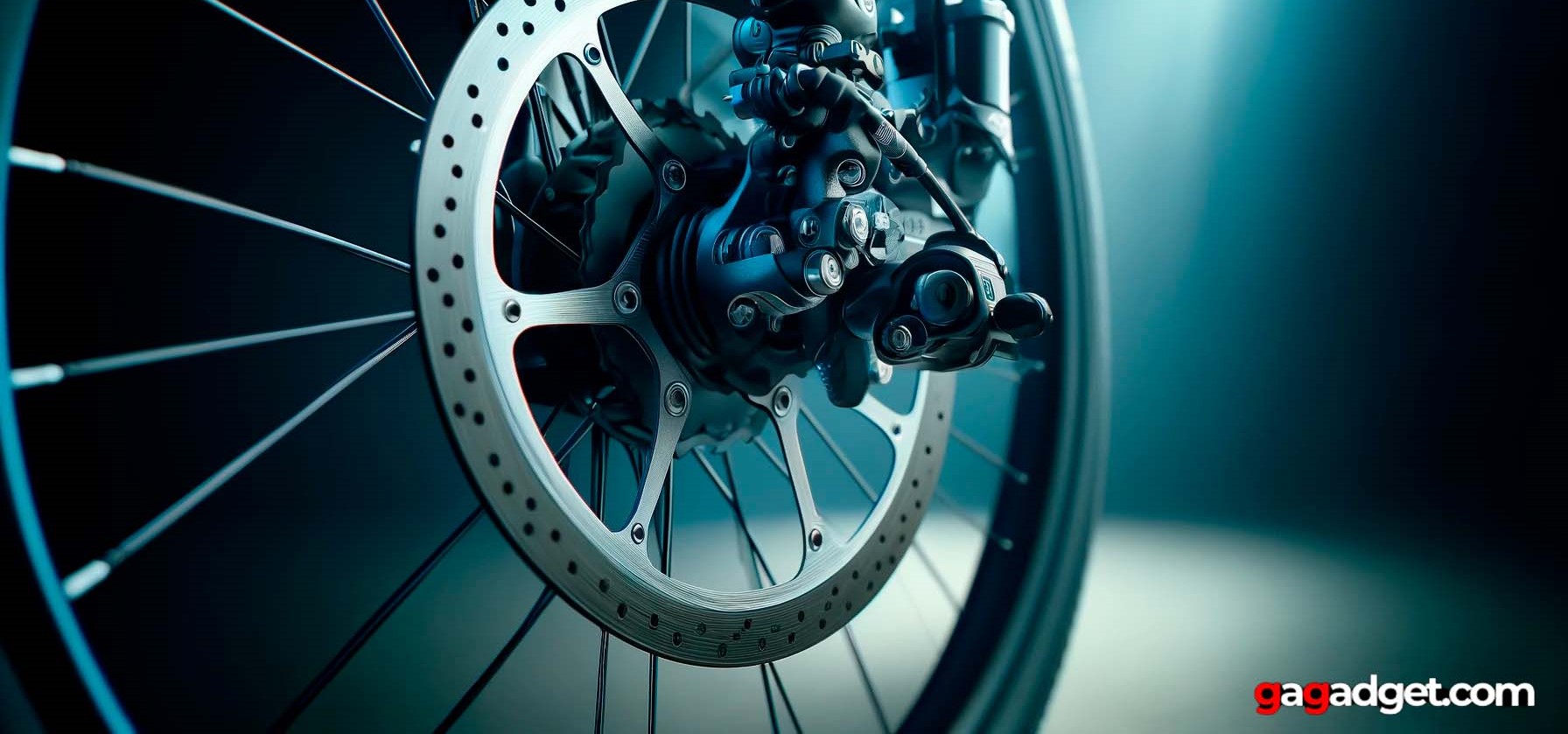

There are two primary types of disc brakes used on e-bikes: mechanical and hydraulic. Each type has its own unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
Mechanical disc brakes use a cable to transfer force from the brake lever to the caliper. When the rider pulls the brake lever, the cable tension increases, causing the caliper to squeeze the brake pads against the rotor, generating friction and slowing down the wheel. Mechanical disc brakes are generally more affordable and easier to maintain than their hydraulic counterparts, making them a popular choice for casual riders and those who prefer a simpler setup. They are also more readily available and can be easily serviced by most bike mechanics.
However, mechanical disc brakes have some limitations. They may require more frequent adjustments to maintain optimal performance, as the cable can stretch over time, affecting the responsiveness of the brakes. Additionally, the cable is exposed to the elements, which can lead to contamination and corrosion, reducing the braking efficiency. Mechanical disc brakes also tend to have a less progressive feel compared to hydraulic brakes, meaning that the force required to stop the bike may not be as smooth or controllable.
Hydraulic disc brakes use a sealed fluid system to transfer force from the brake lever to the caliper. When the rider pulls the brake lever, it pressurizes the brake fluid, which in turn pushes the brake pads against the rotor. This design offers several advantages over mechanical disc brakes. Firstly, hydraulic brakes provide superior modulation, allowing riders to apply the precise amount of braking force needed for a given situation. This level of control is especially beneficial when navigating steep descents or technical terrain.
Hydraulic disc brakes also require less maintenance than mechanical brakes, as the sealed system prevents contamination and the fluid automatically adjusts for pad wear. This self-adjusting feature ensures a more consistent braking feel over time, reducing the need for frequent manual adjustments. Additionally, hydraulic brakes are less affected by cable stretch or contamination, resulting in a more reliable and responsive braking experience.
However, hydraulic disc brakes do have some drawbacks. They are typically more expensive than mechanical brakes due to their complex design and precision components. In the event of a leak or failure, hydraulic brakes can be more challenging to service and may require specialized tools and knowledge. This complexity can be a deterrent for some riders who prefer a more straightforward and user-serviceable system.
Benefits of Disc Brakes on E-Bikes

Disc brakes offer several advantages over traditional rim brakes, making them particularly well-suited for e-bikes:
- Enhanced Stopping Power: Disc brakes provide superior stopping power compared to rim brakes, especially in wet or muddy conditions. This is crucial for e-bikes, which are often heavier and capable of higher speeds than traditional bicycles;
- Better Modulation: Disc brakes allow for more precise control over braking force, enabling riders to make smooth, gradual stops without locking up the wheels;
- Consistent Performance: Unlike rim brakes, which can lose effectiveness in wet weather or when the rims are dirty, disc brakes maintain consistent performance in various conditions;
- Reduced Rim Wear: Since disc brakes act on a separate rotor rather than the wheel rim, they help extend the life of your e-bike's wheels;
- Compatibility with Wider Tires: Disc brakes allow for the use of wider tires, which can improve comfort, traction, and stability on various terrains.
Maintaining Your Disc Brakes
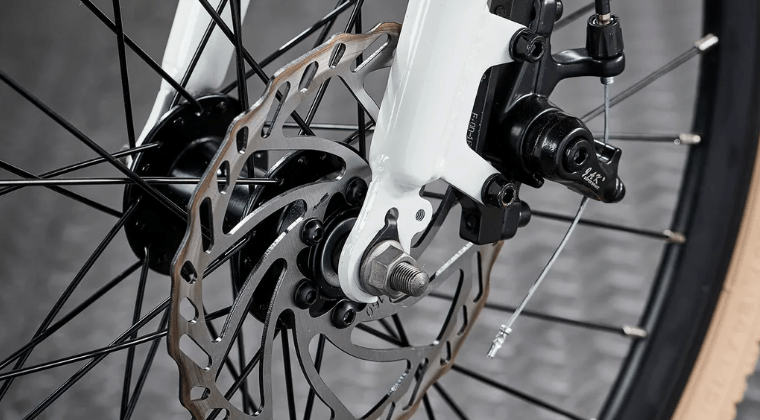
To keep your e-bike's disc brakes performing at their best, regular maintenance is essential. One of the most important aspects of disc brake maintenance is keeping the rotors and pads clean. Over time, brake pads can accumulate dirt, oil, and other contaminants that can reduce their effectiveness and cause annoying squealing or grinding noises. To prevent this, regularly clean your rotors and pads using a dedicated brake cleaner. This specialized solution is designed to dissolve and remove grime without leaving any residue that could compromise braking performance.
Another crucial maintenance task is checking your brake pads for wear. As you use your brakes, the pads gradually wear down, reducing their thickness and effectiveness. Most brake pads have wear indicators, which are small grooves or marks that indicate when the pad material has worn down to a critical level. When your pads reach this point, it's time to replace them. Failing to do so can result in decreased braking performance and potential damage to your brake rotors.
Replacing disc brake pads is relatively straightforward, but it does require some basic tools and knowledge. First, remove the wheel and locate the brake caliper. Next, remove the retaining pin or clip that holds the pads in place, then carefully slide out the old pads. Before installing the new pads, make sure they are compatible with your specific brake model and that the backing plate is facing the correct direction. Once the new pads are in place, secure them with the retaining pin or clip and reinstall the wheel.
In addition to cleaning and replacing pads, it's essential to ensure that your brake rotors are true and aligned with the calipers. A misaligned or warped rotor can cause uneven pad wear, reduced braking power, and annoying rubbing or pulsing sensations when braking. To check your rotors, spin the wheel and watch the rotor as it passes through the caliper. If the rotor wobbles or rubs against the pads at any point, it may need to be adjusted or replaced.
If you have hydraulic disc brakes, there's an additional maintenance task to consider: bleeding the brakes. Over time, small amounts of air can enter the hydraulic system, causing the brakes to feel spongy or less responsive. To fix this issue, the system needs to be bled, which involves removing the air bubbles and replacing the old fluid with fresh, clean fluid. Bleeding hydraulic brakes can be a complex process that requires specific tools and expertise, so it's often best to have this task performed by a professional mechanic.
Finally, if you have mechanical disc brakes, it's important to regularly check and adjust the cable tension. As the brake cables stretch over time, they can cause the brakes to feel loose or less responsive. To fix this, you'll need to adjust the cable tension using the barrel adjusters located at the brake levers or calipers. Consult your e-bike's manual or a professional mechanic for guidance on how to properly adjust your specific brake model.
Disc Brake Maintenance Tips
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Tools Required |
|---|---|---|
| Clean rotors and pads | Every 2-4 weeks or as needed | Brake cleaner, clean cloth |
| Check pad wear | Every 1-2 months | Visual inspection |
| Replace pads | When worn to manufacturer's recommended thickness | Allen wrenches, new pads |
| Align rotors | As needed, if rubbing or noise occurs | Allen wrenches, rotor truing tool |
| Bleed hydraulic brakes | Every 6-12 months or as needed | Bleed kit, hydraulic fluid, allen wrenches |
| Adjust mechanical brake cables | As needed, if brakes feel loose or spongy | Allen wrenches, cable cutters |
Disc Brakes on E-Bikes: FAQ
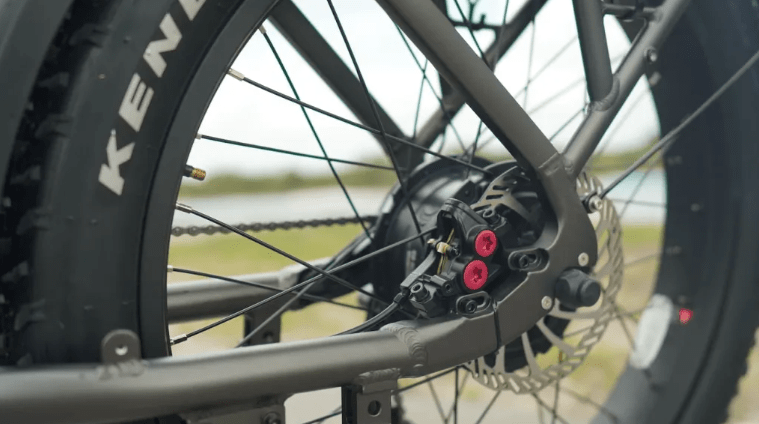
Are disc brakes worth the extra cost on an e-bike?
For most e-bike riders, the benefits of disc brakes, such as improved stopping power, better modulation, and consistent performance in various weather conditions, are well worth the additional cost. However, if you primarily ride in dry conditions and on flat terrain, rim brakes may suffice.
When deciding whether disc brakes are worth the investment, consider your riding style, the terrain you typically encounter, and your personal preferences. If you frequently ride in wet or muddy conditions, tackle steep hills, or carry heavy loads, disc brakes can provide an added level of safety and control. Additionally, if you value a more responsive and adjustable braking feel, disc brakes may be the better choice for you.
Can I convert my e-bike from rim brakes to disc brakes?
In most cases, converting an e-bike from rim brakes to disc brakes is not practical or cost-effective. The frame and fork must be designed to accommodate disc brake calipers and rotors, and the wheels must have compatible hubs. It's generally better to purchase an e-bike with disc brakes if that's your preference.
Converting an e-bike from rim brakes to disc brakes involves more than just swapping out the brake components. The frame and fork must have specific mounts and reinforcements to handle the added stress and torque generated by disc brakes. Without these features, the frame and fork could potentially fail, leading to a dangerous situation for the rider.
Additionally, the wheels must have disc brake-compatible hubs, which are designed to accommodate the rotors and withstand the forces exerted by the calipers. If your current wheels are not disc brake-compatible, you would need to replace them entirely, further increasing the cost and complexity of the conversion.
How long do disc brake pads last on an e-bike?
The lifespan of disc brake pads on an e-bike depends on various factors, including riding conditions, frequency of use, and rider weight. On average, disc brake pads can last anywhere from 500 to 1,500 miles. However, it's essential to check your pads regularly for wear and replace them when necessary.
Several factors can influence the life of your disc brake pads. If you frequently ride in wet or muddy conditions, your pads may wear down more quickly due to the increased grit and debris that can accumulate on the rotors. Similarly, if you ride in hilly or mountainous areas, you may use your brakes more frequently and with greater force, leading to faster pad wear.
The frequency and intensity of your rides also play a role in pad life. If you're a daily commuter or an avid weekend warrior, you'll likely go through pads more quickly than a casual rider who only uses their e-bike occasionally. Additionally, heavier riders or those who carry significant cargo may experience faster pad wear due to the increased demands placed on the braking system.
To extend the life of your disc brake pads, try to avoid unnecessarily dragging your brakes, especially on long descents. Instead, use a combination of intermittent braking and engine braking (using the e-bike's motor resistance) to control your speed. Regularly cleaning your rotors and pads can also help remove debris and contaminants that could accelerate pad wear.
Disc Brakes on E-Bikes: Conclusion
In conclusion, disc brakes have become an essential component of modern e-bikes, offering riders a level of performance and safety that was once unimaginable. By understanding the basics of disc brake technology, the benefits they provide, and the maintenance they require, you can make an informed decision about whether they're right for your riding needs.
And if you do choose an e-bike with disc brakes, you can feel confident knowing that with proper care and attention, they'll be ready to provide reliable, confident stopping power wherever your adventures may take you.
You may also like:
